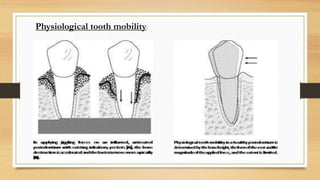
physiologic tooth mobility
Following initial scoring scaling root plan-. In conclusion it is suggested that physiological tooth mobility in primary teeth is estimated objectively by the Dental mobility checker.
A loose tooth that would be uneom-fortable in function.

. Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable. This video is about How to assess TOOTH MOBILITYPdf notes available. From the clinicians standpoint pathologic tooth mobility may be defined as tooth movement that is discernible to the eye.
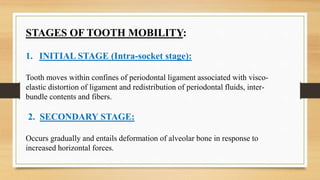
It refers to a moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue. There were also significant differences in tooth mobility among the rest of the stages p. Therefore determining tooth mobility gives useful information for the diagnosis and evaluation of the treatment outcome.
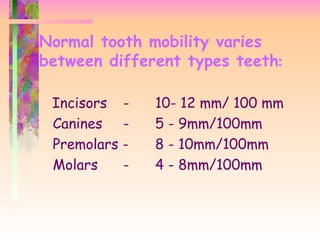
PATHOLOGIC TOOTH MOBILITY When periodontometry is employed values more than 2 standard deviations above the mobility means given in Table 1 are generally regarded as pathologic. PHYSIOLOGIC TOOTH MOBILITY It refers to moderate force exerted on the crown of tooth surrounded by a healthy intact periodontium tooth will show tipping movement until a closer contact has been established between root marginal bony tissue MUHLEMAN1951 KORBER1971 LINDHE 1989 Normal tooth mobility varies between different types teeth. Mobility beyond the physiologic range is termed.
Physiologic dental mobility. Definite to considerable in-crease in mobility but no impairment of function M3. Fixed reference point should be selected eg adjacent tooth that is not mobile and pressure should be applied in horizontal buccal-oral direction to the tooth we are testing.
Generally speaking there is a small amount of physiological. Due to continued jaw growth and passive eruption of surrounding teeth ankylosed teeth will gradually appear to intrude. Article in French Daniel A Aouizerat C Fournier B Brulin H Rassat P Praud J.
Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants. These infections are produced by bacteria originating in bacterial plaque. Physiological tooth mobility seen in healthy teeth depends on the biophysical characteristics of the periodontal tissue whereas pathological tooth mobility is the result of the loss of periodontal support.
Slightly increased mobility M2. Pathologic tooth mobility 1. Tronstad Andreasen Kristerson Clinically teeth lack physiologic mobility and exhibit a metallic tone on percussion.
The abutment mobility of the three types of retainers were all within the mobile ability area except the wrought wire clasp for patient. There was a significant difference in tooth mobility between stage I and stage II p. Measurement of tooth and implant mobility under physiological loading conditions.
By Ramfjord 1959 1967 Tooth mobility was seored as follows. Tooth mobility is a clinical sign that may reflect the degree of periodontal destruction caused by localised infections in the gums and the structures surrounding the teeth ligaments and alveolar bone and providing support and stability. Download link is as follows.
In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. 1077339 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE MeSH Terms Dental Stress Analysis Facial Musclesphysiology Humans Mastication Periodontiumphysiology Toothphysiology Tooth Mobility. Grade 0 mobility Normal physiologic tooth mobility.
Tooth mobility should be determined using two single-ended instruments eg mouth mirror and probe. In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years. Comparing the deflection under load of dental implants with teeth provides valuable input for designing restorations spanning both teeth and implants.
The tooth mobility can be influenced by the quality and quantity of the surrounding periodontal tissues periodontal ligament alveolar bone height and root length which in turn can be influenced by other factors such as type or duration of treatment 2 4. In vivo measurement of the mobility of teeth under physiological loading has been subject of research for years.

Masseter Muscle Musculus Masseter Image Yousun Koh Neck Muscle Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle
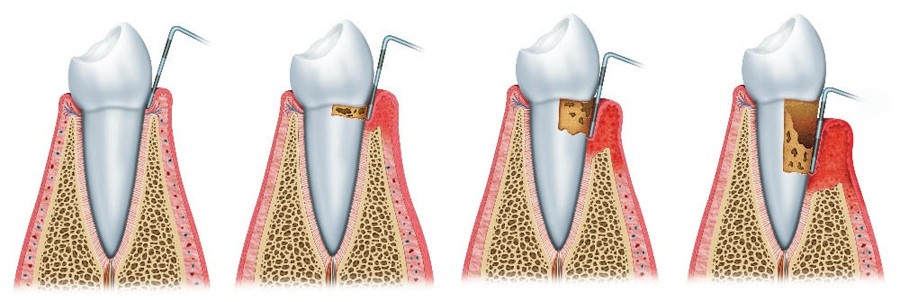
Tooth Mobility And Periodontal Therapy My Dentist Toluca Lake

Body Cavities And Membranes Medical School Studying Nursing School Medical Anatomy
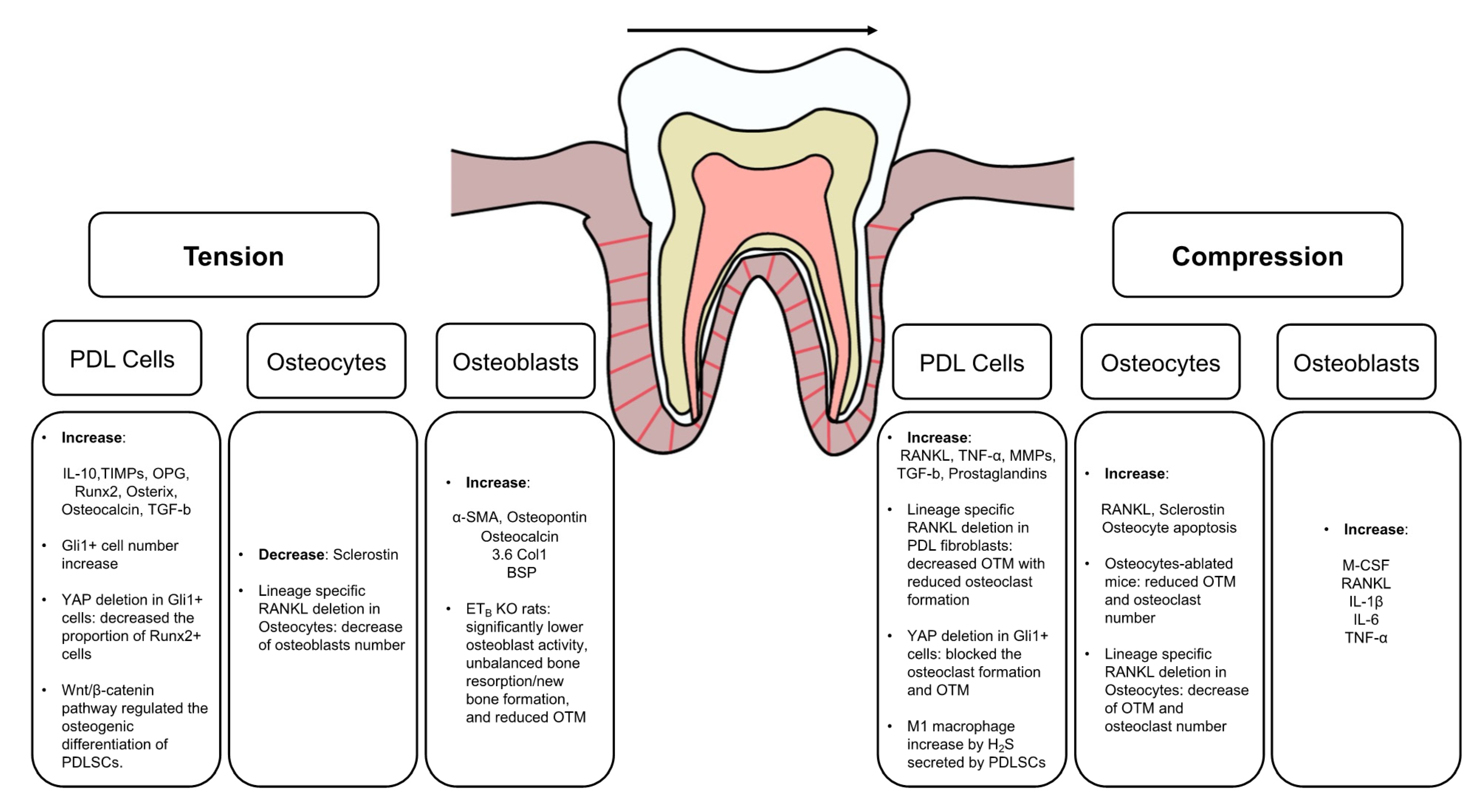
Jcm Free Full Text Mechanistic Insight Into Orthodontic Tooth Movement Based On Animal Studies A Critical Review Html
Tooth Mobility And Periodontal Therapy My Dentist Toluca Lake

Dental Chart Dental Charting Dental Assistant Study Dental Hygiene Student

Orthodontic Tooth Movement The Biology And Clinical Implications Li 2018 The Kaohsiung Journal Of Medical Sciences Wiley Online Library

Natalie S Science Blog Epithelia Tissue And Growth Disorders Squamous Science Blog Tissue

Carnivore Omnivore Herbivore Frugivore Human Spot The Differences Https Www Facebook Com Photo Php Fbid 7511411 Omnivore Carnivores Carnivore Teeth

Effects Of Periodontitis Associated Tooth Mobility With Positive Feedback Download Scientific Diagram








Comments
Post a Comment